Colitis definition and truth!!Colitis refers to inflammation of the inner lining of the colon.
There are many causes of colitis including infection, inflammatory bowel disease, ischemic colitis, allergic reactions, and microscopic colitis.
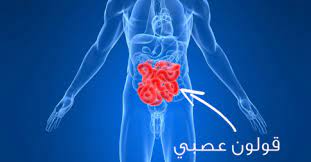
Colitis and colon anatomy!
The colon, or large intestine, is a hollow, muscular tube that processes the products of digestion from the small intestine, removes water, and eventually removes residuals (faeces) through the anus.
This inflammation may be caused by a variety of causes, including the following:
Infections, for example, caused by (parasites, bacteria, viruses)
Loss of blood supply to the colon (ischemia)
Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis)
Allergy
Invasion of the colon wall with white blood cells, lymphocytes or collagen
Symptoms of colitis may include:
Stomach ache
convulsion
Diarrhea, with or without blood in the stool (a characteristic symptom of colitis).
Fever
goosebumps
fatigue
drying
Eye infection
swollen joints
canker sores
Dermatitis.
Blood in the stool is never normal and medical attention should be sought to evaluate the cause.
Depending on the history and physical examination, further tests may be necessary to find the cause of colitis and may include blood tests, urine and stool samples, colonoscopy, and a barium enema.
Treatment for colitis depends on the cause, and often focuses on symptom relief, supportive care, maintaining adequate hydration and pain control.
Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat infectious causes of colitis.
What are the symptoms and signs of colitis?
Colitis causes the muscle layers to go into an intermittent spasm, causing crampy or cramp-like pain that comes and goes.
The pain is usually in the lower abdomen but can be felt anywhere
Since the muscles fail to contract in a normal pattern and colonic contents move rapidly through the colon, there is little chance of water reabsorption.
This leads to watery diarrhea.
If the lining of the colon becomes inflamed and collapses, bleeding may occur. In ulcerative colitis, small ulcers form and cause bleeding.
Pain before, during, or after an episode of diarrhea
With colitis, especially colitis involving the distal colon (rectum and sigmoid colon), pain often precedes and causes a bowel movement to cause diarrhea.
After a bowel movement, the pain may subside but then return with the next episode of diarrhoea.
Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease may be associated with symptoms outside the colon due to the body itself attacking other organs, such as:
swollen joints
eye inflammation (uveitis),
canker sores in the mouth (aphthous ulcers),
Dermatitis (pyoderma).
When should someone call a doctor about colitis?
If diarrhea persists for more than two to three weeks, or if there is blood in the stool or fever, or if the person has signs of dehydration.
Blood in the stool is not normal and should always be evaluated.
Lightheadedness (dizziness), especially when changing from a sitting or lying position to a standing position (orthostatic hypotension).
weakness
dry mouth
dry eyes
decreased urine output
A high temperature associated with diarrhea may be a warning sign of a major infection.
Abdominal pain is not normal, and although diarrhea may be associated with mild cramping, the presence of increased abdominal pain requires the need to seek immediate medical attention.
What kind of doctor diagnoses and treats colitis?
Most of the time colitis is treated by a primary health care provider or an internal medicine specialist, especially when colitis is first diagnosed and the cause is uncertain.
Once the cause is found, the health care provider may be the only person required to continue care. If further examination and diagnostic tests are needed, specialists, such as a gastroenterologist, may be consulted.
If an infection is the cause of colitis, an infectious disease specialist may be consulted. In some cases, other specialists, such as surgeons and interventional radiologists, may be involved in treatment
What is the treatment for colitis?
Medications are often used to control inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and medication is chosen for the individual patient.
Antibiotics are commonly used only if specific bacteria are isolated and treatment is known to shorten the course of infection.
Over-the-counter medicines to treat diarrhea should be used with caution, especially if there is abdominal pain and fever.
It is always wise to check with your care provider or pharmacist before taking antidiarrheal medication.
Surgery is not usually a treatment option for most causes of colitis.
What foods help soothe colitis?
Since clear liquids tend to be absorbed mostly in the stomach and small intestine, initially avoiding solid foods and promoting a clear liquid diet may help rehydrate the body and rest the colon.
Changing your diet to reduce symptoms or flare-ups may help relieve symptoms of the disease, but there is no cure for some forms of colitis.
What foods should I avoid if I have colitis?
The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation of America recommends avoiding the following foods if you have colitis: fatty or fried foods
Milk or products containing milk
Some foods rich in fiber such as popcorn, seeds, nuts, and corn
People with lactose intolerance should avoid dairy products that contain lactose.
There are a variety of companies (such as Lactaid and Green Valley Organics) that offer lactose-free products such as yogurt, yogurt, ice cream, and cheese.
Is colitis related to shortness of breath or not?!
Flatulence occurs when the abdomen feels tight or full.
This may cause the area to appear visually larger.
The abdomen may feel firm or tight to the touch, and it can cause discomfort and pain.
Dyspnea is difficulty breathing. It is the feeling that you cannot catch your breath, that you are not taking in enough air.
It can cause a feeling of fainting and panic if it continues for a long time
Therefore, colitis causes flatulence, which may sometimes cause shortness of breath and lack of comfort, and thus there is a relationship between colitis and shortness of breath.
about the author
nutritionist Shaimaa Ali
is a-freelance journalist specializing in health and fitness as well as nutritionist certified from mansoura university on Egypt
for Medical information i recommended National Institutes of Health Most of My blog source by it
Explore link https://www.nia.nih.gov
kindly check with a doctor in addition to using the app and before making medical decisions